RENEWABLE AND NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCES
Ecology is the study of man and his environment. The natural
environment contains all natural resources that are necessary for life: the
air, the oceans, the sun and the land. Because these resources are vital
for life, ecologists study their importance and how to use them carefully.
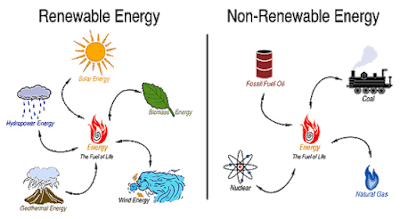
Ecologists often divide resources into two groups: renewable and
non-renewable. When we use a resource, it takes some time to replace
it. If we can replace the resource quickly, it is called renewable. It is
non-renewable if we cannot replace it quickly and easily. For example,
grass for animals is a renewable resource. When animals eat the grass,
usually more grass will grow. Coal, however, is non-renewable
because it takes millions of years to make coal. All fossil fuels are
non-renewable resources. The decomposition, or decay, of organic
materials forms fossil fuels and they include coal, oil and gas. We
started using these fossil fuels in large quantities less than 200 years
ago and we haven't stopped since. Some scientists now predict that we
will exhaust our supplies of fossil fuels in 50 years. In other words, in
50 years there won't be any fossil fuels left.
Many resources are non-renewable. As a result, we must conserve
them. That is, we must use them carefully. There are several ways to do
this. First, we must find and use new resources. Second, we should
find new uses for old resources. Third, we shouldn't waste any
resources. Last, we must try to recycle the already available resources.
In this way, we can use the same material over and over again